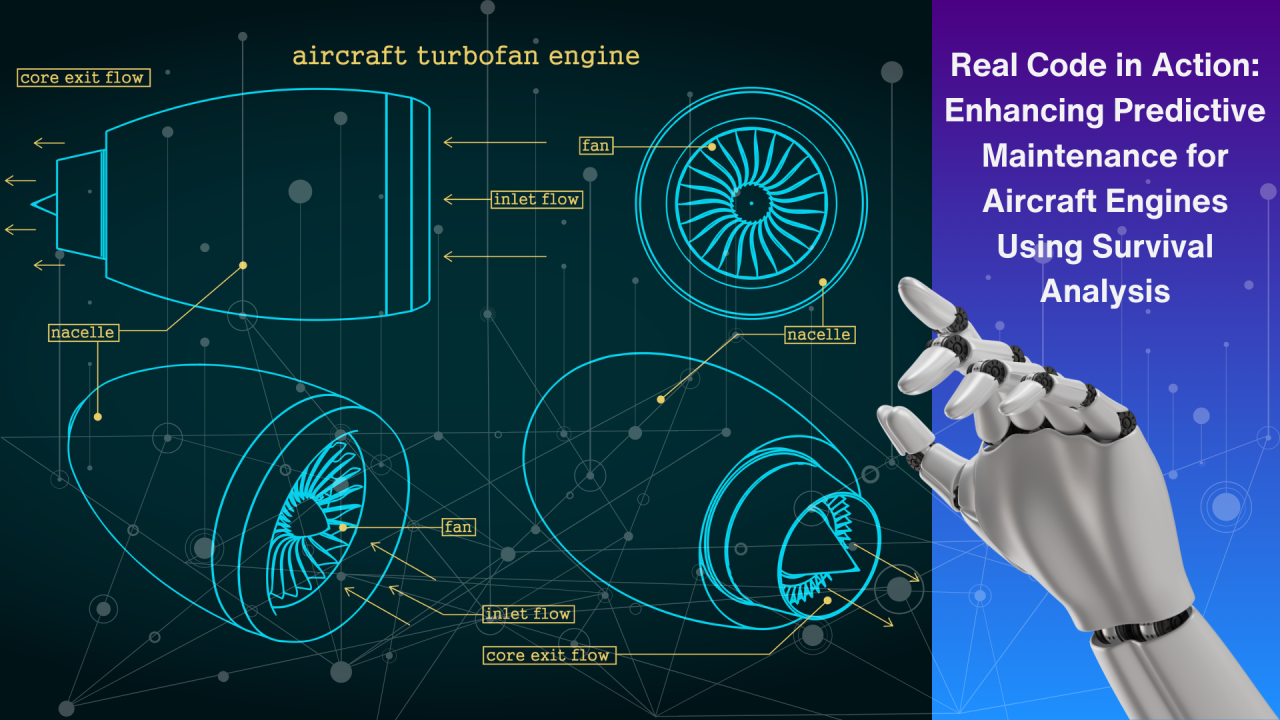
Modern engines operate under high thermal and mechanical stress, making maintenance a crucial factor in overall performance, fuel efficiency, and component longevity. As industries push for higher output and reduced emissions, maintaining engine systems becomes more than a routine task—it becomes a strategic approach to maximising operational success. Preventative maintenance is one of the most cost-effective ways to achieve this, helping businesses avoid catastrophic failures and improve long-term reliability.
The Role of Thermal Management
Effective thermal management lies at the heart of engine efficiency. Excessive heat not only degrades components but also reduces combustion quality and increases overall emissions. Cooling systems, intercoolers, oil pathways and airflow mechanisms must all function optimally to balance temperature across the engine. If any of these systems operate below peak capacity, it creates a ripple effect throughout the engine assembly.
Heat buildup can warp components, accelerate corrosion, and place undue pressure on gaskets and seals. Conversely, when a cooling system is maintained correctly, the engine can operate closer to its designed efficiency levels, resulting in better fuel economy and less mechanical wear.
Preventative Maintenance as a Performance Strategy
Maintenance is often misunderstood as a reactive task performed when issues arise. In reality, forward-thinking businesses are integrating maintenance into their performance strategy. By implementing structured inspection routines, they reduce unexpected downtime, improve safety, and extend engine lifespan.
Predictive and preventative maintenance technologies—including thermal imaging, vibration analysis and sensor-based performance tracking—are increasingly being used to identify potential problems before they escalate. This approach helps detect early signs of imbalance, contamination, or heat-related stress, allowing operators to intervene at the optimal moment.
Keeping Air and Fuel Pathways Clean
One of the most overlooked aspects of engine performance is the quality of the airflow and fuel delivery systems. Over time, deposits accumulate due to impurities, oil vapour and environmental contaminants. When these deposits are left unchecked, they can influence air density, temperature consistency and combustion timing.
This is particularly true for components such as intercoolers, manifolds and charge air pathways. For example, industries often rely on charge air cooler cleaning as part of their preventative routine, ensuring that airflow temperature remains stable and that the engine receives the optimal mix for efficient combustion. Even a small reduction in airflow efficiency can significantly impact performance and increase fuel usage.
Reducing Emissions Through Proper Maintenance
With environmental regulations tightening across global industries, engine maintenance is becoming an essential part of emissions control. Clean systems burn fuel more completely, reducing particulate levels and harmful exhaust gases.
Maintaining core components ensures engines are operating within regulated limits without compromising power or reliability. Companies that prioritise maintenance also strengthen their compliance position, reducing the risk of penalties or costly retrofits.
Technology Trends in Engine Maintenance
The maintenance landscape is changing rapidly thanks to digital tools, cloud diagnostics, and real-time performance monitoring. Sensors embedded in critical components feed engine health data directly to operators, allowing for immediate intervention when anomalies appear.
Furthermore, AI-assisted maintenance planning is gaining traction, using historical data patterns to predict component failures. This not only avoids costly breakdowns but also allows maintenance teams to plan labour and parts procurement more efficiently.
Why Preventative Maintenance Protects Profitability
An engine failure doesn’t just result in repair costs—it causes downtime, production delays, staff inefficiencies and potential safety risks. A well-executed preventative maintenance plan reduces:
- Unexpected breakdowns
- Fuel consumption
- Repair frequency
- Equipment replacement costs
- Compliance concerns
Over time, these savings can compound significantly, making preventative maintenance a clear strategic advantage.
Looking Ahead
With industries seeking ways to increase output while maintaining sustainability commitments, preventative maintenance offers a direct and measurable pathway to improvement. Clean systems, precise airflow, efficient thermal management and early fault detection all contribute to more reliable and environmentally friendly operations.
Continued innovation in sensor technology, digital analytics and thermal engineering will make maintenance even more efficient in the future, allowing companies to capture even greater performance gains.